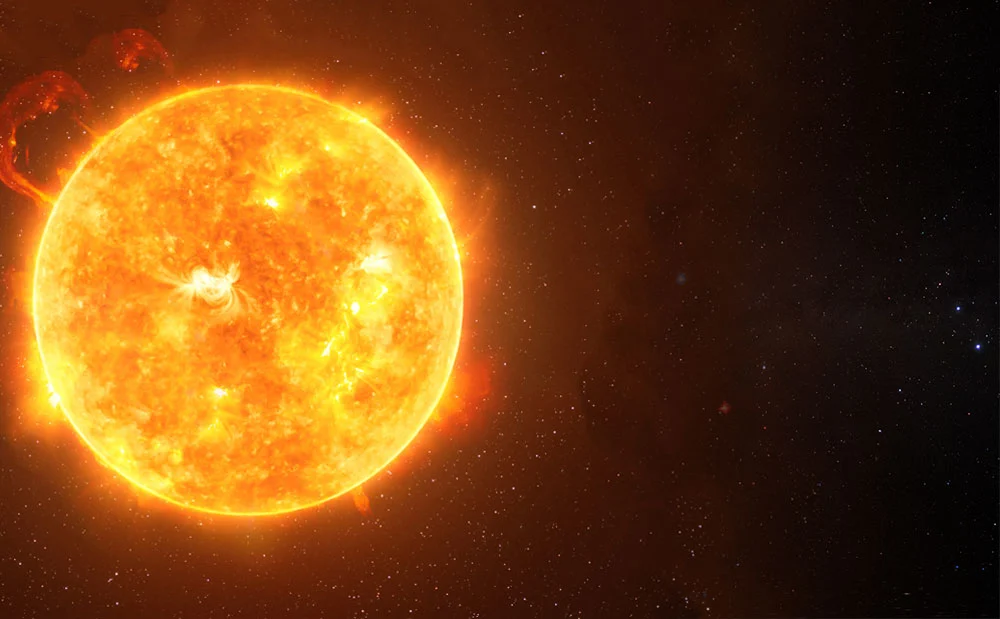
Sol
The sun is the star at the center of our solar system and the primary source of light and energy for our planet. It is a massive ball of hot, glowing gas, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. The sun is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) away from Earth and is so massive that it makes up about 99.8% of the mass of our solar system. The sun is a G-type main-sequence star, which means it is in the middle of its life cycle and is fusing hydrogen atoms into helium in its core. This process releases a vast amount of energy in the form of light and heat, which Earth receives as sunlight.

Mercury
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system, located closest to the sun. It has a rocky surface, similar to Earth's moon, and no moons of its own. Mercury has a very thin atmosphere and experiences extreme temperatures, with daytime temperatures reaching up to 800 degrees Fahrenheit and dropping to -290 degrees Fahrenheit at night. Due to its proximity to the sun, Mercury has a short year of only 88 Earth days, and a day that is longer than its year, taking 59 Earth days to rotate once on its axis.

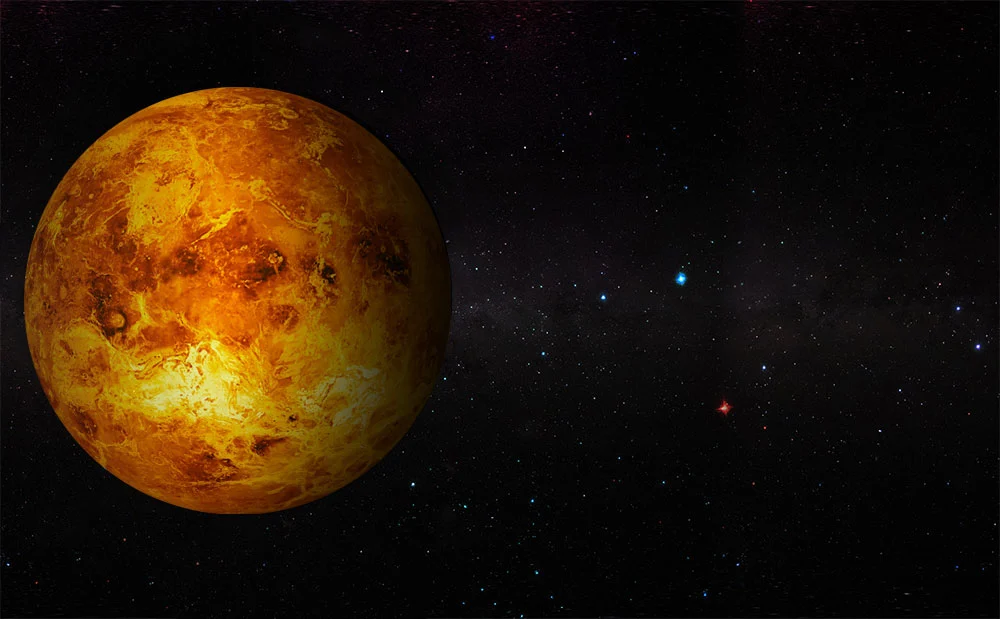
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the sun and is known as Earth's "sister planet" due to their similarities in size, composition, and proximity. However, Venus is a hostile environment with a thick, toxic atmosphere of carbon dioxide that traps heat, making it the hottest planet in our solar system. Surface temperatures can reach up to 900 degrees Fahrenheit, causing the planet to be uninhabitable for humans. Venus has no natural satellite and rotates in the opposite direction to most other planets. It is also the brightest object in the night sky, aside from the moon and the sun.
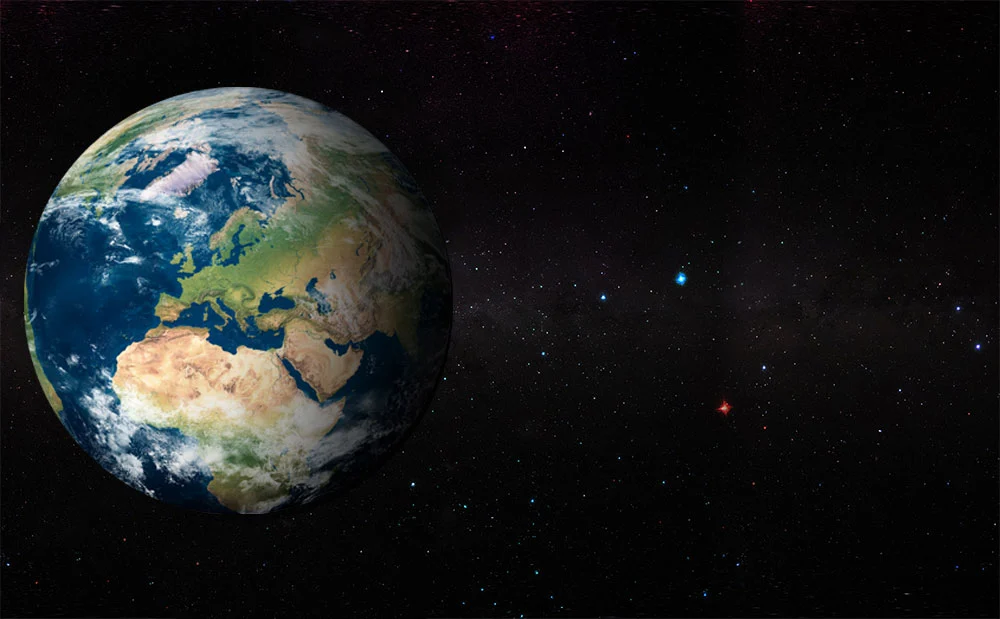
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the sun and the only known planet to support life. It has an atmosphere that contains oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide, which are essential for life. It has a solid surface with continents, oceans, and diverse ecosystems that are home to millions of species. Earth's rotation causes day and night, and its orbit around the sun takes one year to complete. It is also surrounded by a magnetic field that protects it from harmful solar radiation. Humans have a significant impact on Earth's environment and climate, and it is crucial to protect and conserve our planet for future generations.

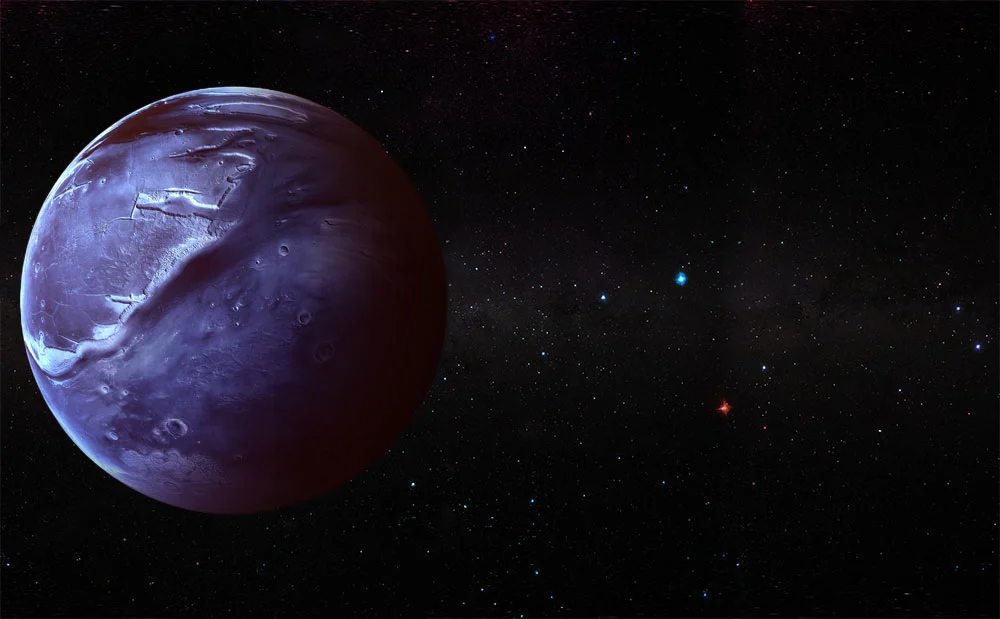
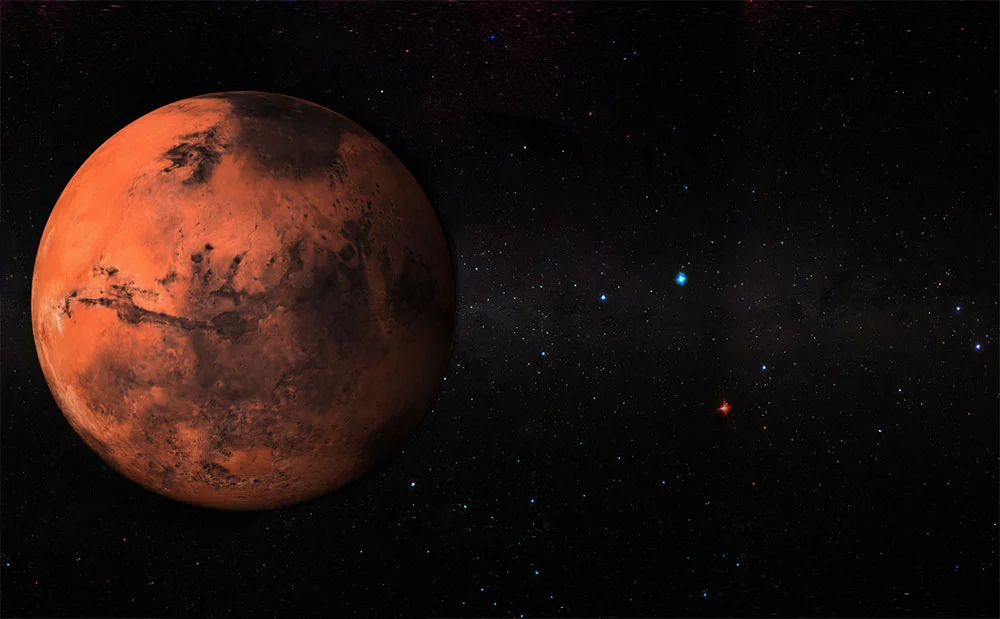
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet in our solar system and is known as the "red planet" due to its reddish appearance. It has a thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide, and its surface is covered with mountains, valleys, and large canyons. Scientists believe that Mars had a warmer and wetter past, and have found evidence of the possibility of microbial life on the planet. It is also being explored by several missions, including the Mars rovers and planned human missions in the future. Understanding Mars is important in our search for habitable planets beyond Earth.

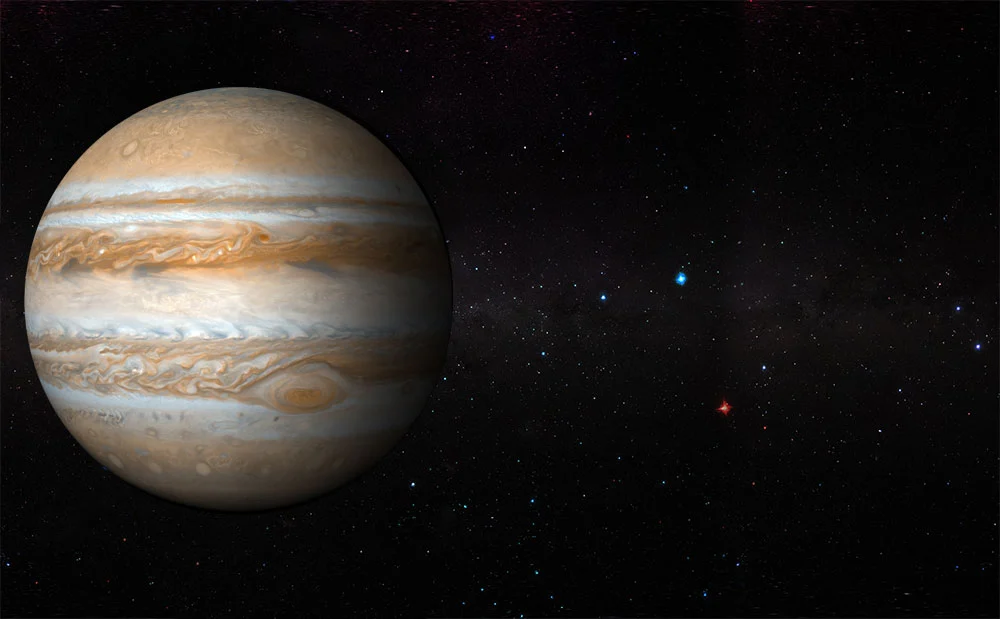
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the sun and the largest planet in the solar system, with a diameter of about 86,881 miles. It is a gas giant with a thick atmosphere composed of hydrogen and helium, and it has at least 79 moons. The iconic feature of Jupiter is the Great Red Spot, a massive storm with winds of up to 400 mph that has been raging for centuries. Jupiter also has a powerful magnetic field and many swirling, colorful cloud formations. It is a popular subject of study for astronomers and space probes alike.

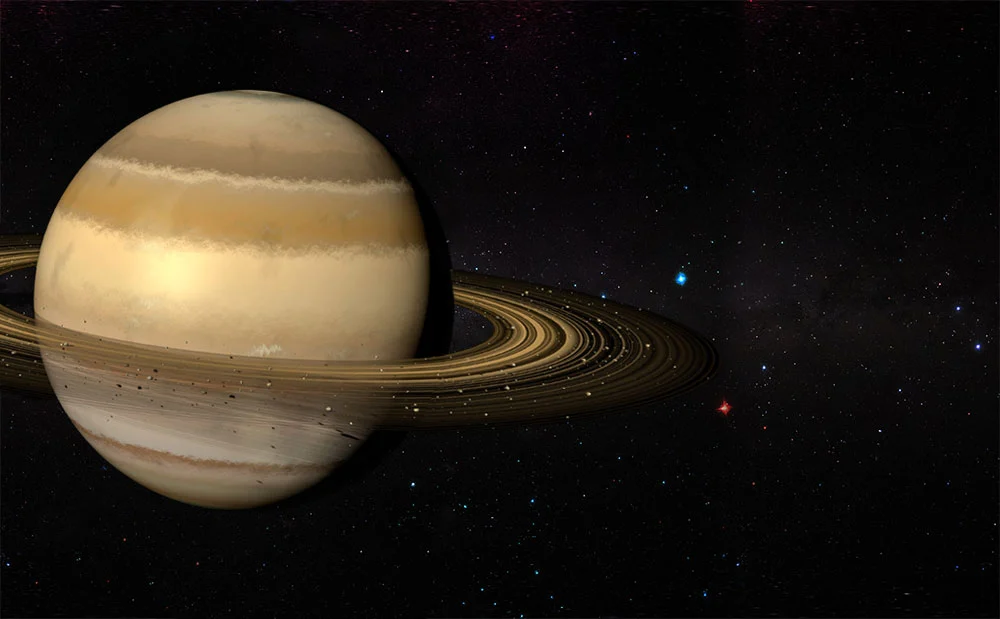
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest planet in our solar system. It is known for its distinctive rings made up of ice particles and rocks that orbit around the planet. Saturn's atmosphere is mostly hydrogen and helium, and it has dozens of moons, including the largest, Titan. The planet has been visited by spacecraft such as Voyager 1 and Cassini-Huygens, which have provided important insights into its atmosphere, magnetic field, and moons. Saturn takes about 29 years to orbit the Sun and spins on its axis in just over 10 hours.

Uranus
Uranus is an icy giant planet that was discovered in 1781 by William Herschel. It's known for its tilted axis of rotation, which causes extreme seasons on the planet. This tilt also leads to some very unusual weather patterns and atmospheric phenomena. Uranus has a system of 27 known moons and a ring system, but no solid surface like Earth.

Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in our solar system. It is a gas giant planet, meaning it is primarily composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane gases. It was discovered in 1846 by German astronomer Johann Galle and Heinrich d'Arrest. Neptune orbits the Sun at an average distance of about 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion kilometers), taking about 165 Earth years to complete one orbit. Its orbit is slightly eccentric, which means its distance from the Sun varies slightly throughout the year.

